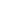
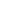
M7P H7 LED headlight bulb internal structure anatomy
The product uses a good heat dissipation copper tube to circulate heat.
The heat is transferred downward from the lamp head
After the last cycle, the heat is discharged through the fan
M7P H7 LED headlight bulbs, like many high-performance LED headlight bulbs, are designed with efficient heat dissipation in mind, as LEDs can produce a significant amount of heat that needs to be managed for optimal performance and longevity. Here’s a general anatomy and how the heat dissipation works based on your description:
### Internal Structure Anatomy:
1. **LED Chip(s):** At the heart of the bulb is the LED chip, which is responsible for producing light. The M7P H7 bulb likely contains one or more high-brightness LED chips.
2. **Heat Sink:** Surrounding the LED chip is a heat sink, often made from aluminum or another highly conductive material, to draw heat away from the chip. In the case of the M7P H7, you mentioned a copper tube, which is an excellent thermal conductor and would serve as part of the heat sink system.
3. **Copper Tube Heat Pipe:** This is a key feature in the M7P H7. A heat pipe is a passive heat transfer device that efficiently transfers heat from the source (the LED) to a location where it can be dissipated. It works by using a small amount of liquid (often water or alcohol) that evaporates at the hot end (near the LED), travels through the tube, and condenses at the cooler end, releasing the heat. The liquid then returns to the hot end via capillary action, allowing the cycle to repeat.
4. **Fan (Active Cooling):** After the heat has been transferred to the lower part of the bulb via the copper heat pipe, a small fan actively cools the area by drawing air over the heat sink, thus dissipating the heat into the surrounding environment. The fan is powered by the electrical circuitry of the bulb and is typically only active when the bulb is on and generating heat.
5. **Driver/Controller Circuitry:** The LED requires a specific voltage and current to operate, and this is managed by a driver or controller circuit. This circuit also controls the fan, turning it on when the temperature reaches a certain threshold.
6. **Base and Connector:** The base of the bulb is designed to fit into the standard H7 socket of the vehicle. It includes the electrical contacts necessary to connect the bulb to the car’s electrical system.
### Heat Dissipation Process:
- **Heat Generation:** When the LED is powered on, it generates both light and heat.
- **Heat Transfer:** The heat is immediately conducted away from the LED chip by the copper tube, which acts as a heat pipe.
- **Heat Distribution:** The heat is distributed along the length of the copper tube and towards the heat sink.
- **Heat Dissipation:** The fan draws air over the heat sink, cooling the copper tube and the heat sink, and expelling the heat out of the bulb assembly.
- **Continuous Cycle:** As long as the bulb is on, the cycle of evaporation, condensation, and air cooling continues, ensuring the LED operates within a safe temperature range.
This design ensures that the LED remains cool enough to function properly and to extend its lifespan, while also providing bright and consistent lighting for the vehicle.
Post time: Jun-27-2025